Parametric Blending
Sup 189
40% In work
This supplement introduces Parametric Maps to store the quantification
of a specific measurement.
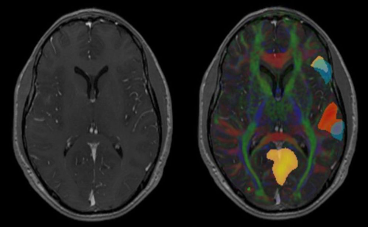
The Parametric Blending Presentation State is defining the blending of
the content of the different Parametric Maps with optionally an
anatomical image as underlay.
This way showing the measurements (like BOLD fMRI, Diffusion parameter
maps, CT/MRI Perfusion parameter maps, FDG PET map) in relation to the
anatomical structure.
Displayed Area and Graphic modules are present to allow the user to
add graphical information related to the blending operation. Like
marking the Motor Cortex based on the parametric map.
The usage will be described by using an example of an fMRI study in a
new chapter in PS 17 as Informative Annex.
A suggestion was raised to consider the concept of enhanced blending
and display pipeline from ultrasound (See DICOM Part 3 and Part 17). A
graph illustration helps the implementers greatly.
A discussion took place regarding if this supplement leans toward
dynamic controlling or more final frozen presentation states. The
suggestion from working group 6 was to go for dynamic behavior.
In November the plan is to get toward ready for public comments.
View details »
View overview slides »
Patient Radiation Dose
Sup 191
60% before Letter Ballot
This Supplement describes a structured report, which records the
estimated radiation dose to a patient.
The supplement includes radiation dose from CT, projection X-Ray, and
radiopharmaceutical administration (diagnostic and therapeutic).
Occupational radiation exposures and dose from external beam therapy,
ion beam therapy, or brachytherapy is out of scope.
There are multiple methodologies and models that can be used to
estimate patient dose and these methods are rapidly changing.
Yet, once an estimate of the radiation dose absorbed by a patient is
performed, the storing and transferring in a standard format is needed
for the radiation source data, method used, parameters used within the
method and the resulting dose estimate.
The approach taken here for the Patient Radiation Dose Structured
Report (P-RDSR) is to define a new Structured Report (SR) object
template and SOP Class.
This SR object, independent of the images or the MPPS, could be routed
to an appropriate Dose Information Reporter System.
Slides were presented reflecting the current state of the concept
discussions. Especially the goals of flexibility for the Patient Dose
SR were made clear:
Store the results of Patient Organ Dose calculations:
- Store a SINGLE procedure or MULTIPLE procedures
- Including one or more modalities and procedure steps/phases
- One or more organs
- One or more calculation methods
A discussion took place on which grouping to use. Possibilities
include grouping on organ, grouping on method used and
combinations. There was no final conclusion.
A line by line review from the beginning of the document was started.
In November the plan is to get ready for letter ballot voting.
View details »
View overview slides »
Protocol Approval
Sup 192
70% Letter Ballot
This Supplement defines a storage SOP Class to record and convey
approval (or disapproval) of DICOM Defined Procedure Protocol
instances.
The nature, basis and scope of the approval depends on the semantics
of the codes used in the assertion.
Specific codes and examples are provided for assertions about CT
Protocols.
Constraints (how strict shall a protocol be?) regarding families of
scanners and reusing protocols triggered a discussion.
This lead to the problem space of matching scanner models/families
with the scope of protocols within an institution.
Further the use of the clinical trial module for experimental
procedures outside clinical trials was suggested to be described.
The question arose which level of detail and structure to document
regarding approval: Clinic, institution, department and hierarchy of
responsibility.
The supplement was voted to go out for letter ballot voting.
View details »
View overview slides »